New paper published in Journal of Cachexia

Dysferlinopathy, also known as LGMD R2, is a type of muscular dystrophy caused by the absence of a protein called dysferlin. This protein is essential for repairing muscle fibres when they get damaged. In healthy muscles, sodium levels are normally low at rest but temporarily increase during contraction, returning to normal once the muscle relaxes.
This study looked at how sodium levels behave in the muscles of people with dysferlinopathy compared to healthy individuals. Using a special type of MRI that measures sodium, we found that people with dysferlinopathy have higher sodium levels in their muscles even at rest, which may indicate ongoing muscle damage. After exercise, healthy individuals showed a temporary rise in sodium that returned to normal, but in dysferlinopathy patients, sodium levels stayed high and did not recover in the same way.
These findings suggest that sodium MRI could be a useful tool for tracking muscle health in people with muscular dystrophy. By detecting changes in sodium levels, this technique may help identify early signs of muscle damage, monitor disease progression, and assess how well new treatments are working.
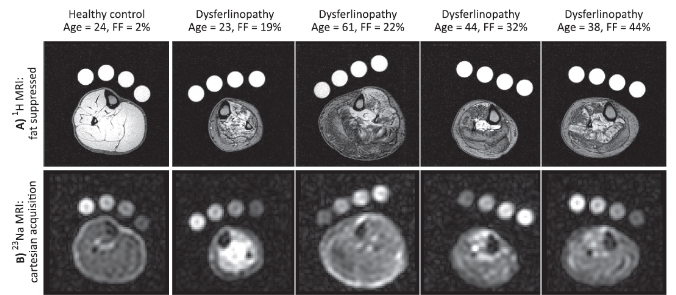
The below image compares lower leg muscle scans from a healthy person (1st column) and individuals with dysferlinopathy (2nd to 5th columns). The top row (A) shows fat content in muscles. Healthy muscle appears bright and well-defined, while dysferlinopathy muscles show increasing dark areas, indicating fat replacement. The fat fraction (FF) reflects disease progression, with higher percentages showing more fat buildup.
The bottom row (B) shows sodium MRI scans. Healthy muscle appears darker and uniform, while muscles with dysferlinopathy show brighter areas, indicating higher sodium levels.
Author(s)

Carla Bolaño Diaz