Preclinical Drug Testing
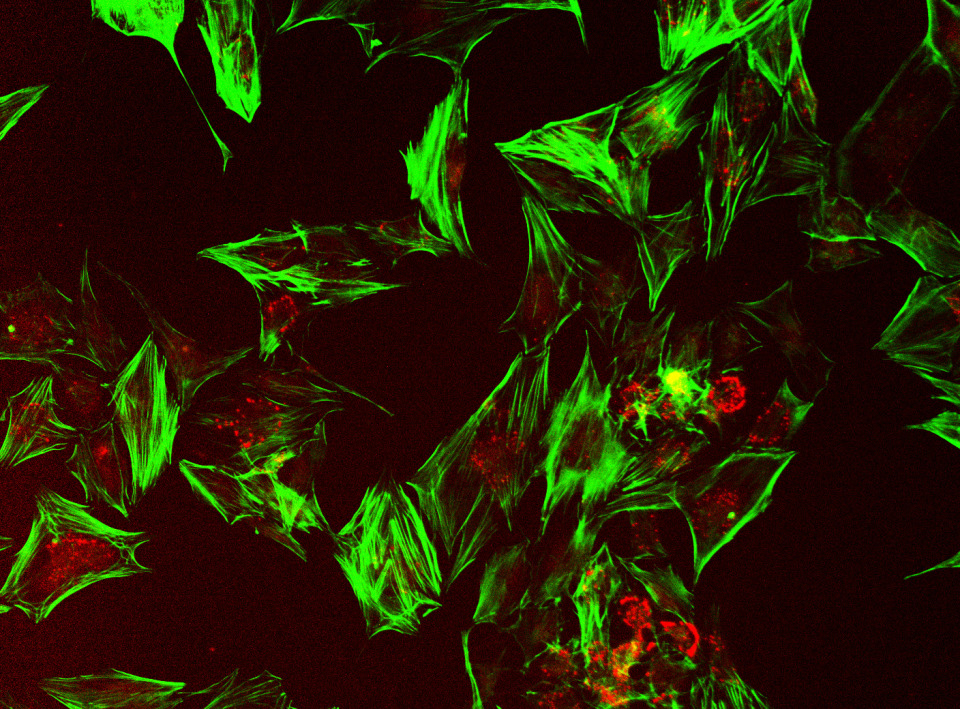
At JWMDRC, we have developed a state-of-the-art in vitro screening platform that models the fibroadipogenic progenitor (FAP) differentiation process — capturing the transition towards fibrotic or adipogenic lineages in the context of muscle wasting. This technology was described in Strategy for drug repurposing in fibroadipogenic replacement during muscle wasting: application to Duchenne muscular dystrophy (doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1505697; PMID: 40206397; PMCID: PMC11979640)
Using this system, we can evaluate how candidate molecules influence FAP differentiation, provide mechanistic insight into signalling circuits, and help prioritise repurposed (or novel) small molecules for downstream development.
What we offer to Industry Partners
| Service | Description | Benefit to Partners |
|---|---|---|
| High-throughput drug repurposing screens | We can test libraries of approved/clinical compounds for their ability to modulate FAP fibrogenesis or adipogenesis (using human and disease-relevant cell models). | Rapid identification of “hits” that may slow or reverse fibroadipogenic replacement in muscle disease |
| Dose–response / confirmation screens | For selected hits, we perform more detailed dose–response studies and validate effects in human FAPs (from healthy donors and disease patients). | Greater confidence in translational relevance |
| Mechanism-of-action / pathway mapping | Integration of proteomic and transcriptomic data (from public or partner sources) to map how a compound modulates signalling circuits and mechanistically link phenotypic effects to molecular pathways. | Insight for target deconvolution, lead selection, biomarker hypothesis generation |
| Customized assay development & optimization | We can adapt or extend the platform (e.g. use of patient-derived FAP lines, co-culture systems, orthogonal readouts) to suit specific industry needs. | Flexibility to support proprietary pipelines |
| Consultation & collaborative design | We offer joint protocol development, experimental design, and interpretation support — ensuring that your preclinical plans are aligned with mechanistic rigour and translational potential | Leverage JWMDRC’s domain expertise and track record in neuromuscular disease |
Why partner with the JWMDRC?
-
Domain expertise in neuromuscular disease:
As part of the John Walton Muscular Dystrophy Research Centre, we bring deep knowledge of muscle biology, rare neuromuscular disorders, and how fibroadipogenic replacement contributes to disease progression. -
Human-relevant cellular systems:
Our models use human FAPs (immortalized and primary) and integrate omics-level comparisons to patient data to ensure biological relevance.
-
Efficiency & cost-effectiveness:
By focusing on repurposing pipelines and leveraging robust screening infrastructure, we can reduce time and cost in early-stage decision making. -
Translational prioritization:
Because our platform links phenotypic effects to mechanistic pathways and maps to patient-derived omics signatures, we help de-risk lead selection and strengthen translational confidence.
Use cases & potential applications
- Pharmaceutical or biotech companies seeking to identify repurposing opportunities for compounds in muscle wasting, muscular dystrophy, sarcopenia, or cachexia.
- Partners exploring adjunctive therapies to reduce fibro-adipogenic replacement in degenerating muscle, thereby improving efficacy of regenerative or gene therapies.
- Organizations looking to validate mechanistic hypotheses (e.g. signalling modulation of FAP fate) or to generate biomarker hypotheses from pathway-level insights.
- Drug discovery groups needing customized differentiation assays or mechanistic screens in muscle-relevant progenitor systems.